The development trend of the Internet of things is also generally optimistic and concerned, but the networking of embedded devices will greatly increase the complexity of software. The traditional embedded RTOS kernel has become more and more difficult to meet the needs of the market. In this case, the concept of Internet of things operating system should be put into operation. At present, IOT operating systems are mainly divided into two categories. One is developed from the traditional embedded RTOS, and the other is extended from the cloud platform of Internet companies. This paper will make an inventory of the existing active IOT operating systems
Each era has its own characteristics of electronic products, and each type of products has its own adaptive operating system. For example, the early multi tasking operating systems such as MULTICS and UNIX, to the multiprocessor operating systems such as Linux and windows adopted by personal computers, and then to the mobile operating systems such as IOS and Android in the era of smart phones.
These operating systems run at the lowest level of 'bare metal' equipment and build the environment and platform for the operation of other software and Applications (APPs). Nowadays, the popularity of various software and Internet applications, as well as the brilliance of the PC era and the mobile Internet era, are inseparable from the perfect operating system.
In recent years, with the rapid development of the Internet of things (IOT) market, embedded device networking has become a new demand. The core and foundation of the Internet of things is still the Internet, but unlike the Internet, which emphasizes the interconnection between people, the Internet of things extends and expands the connection network between people and things, things and things, forming what we call 'the interconnection of all things'.
Although the development of the Internet of things is the general trend and is generally favored and concerned, the networking of embedded devices will greatly increase the software complexity. The traditional embedded RTOS (real-time operating system) kernel has become more and more difficult to meet the needs of the market. In this case, the concept of Internet of things operating system (IOT OS) came into being.
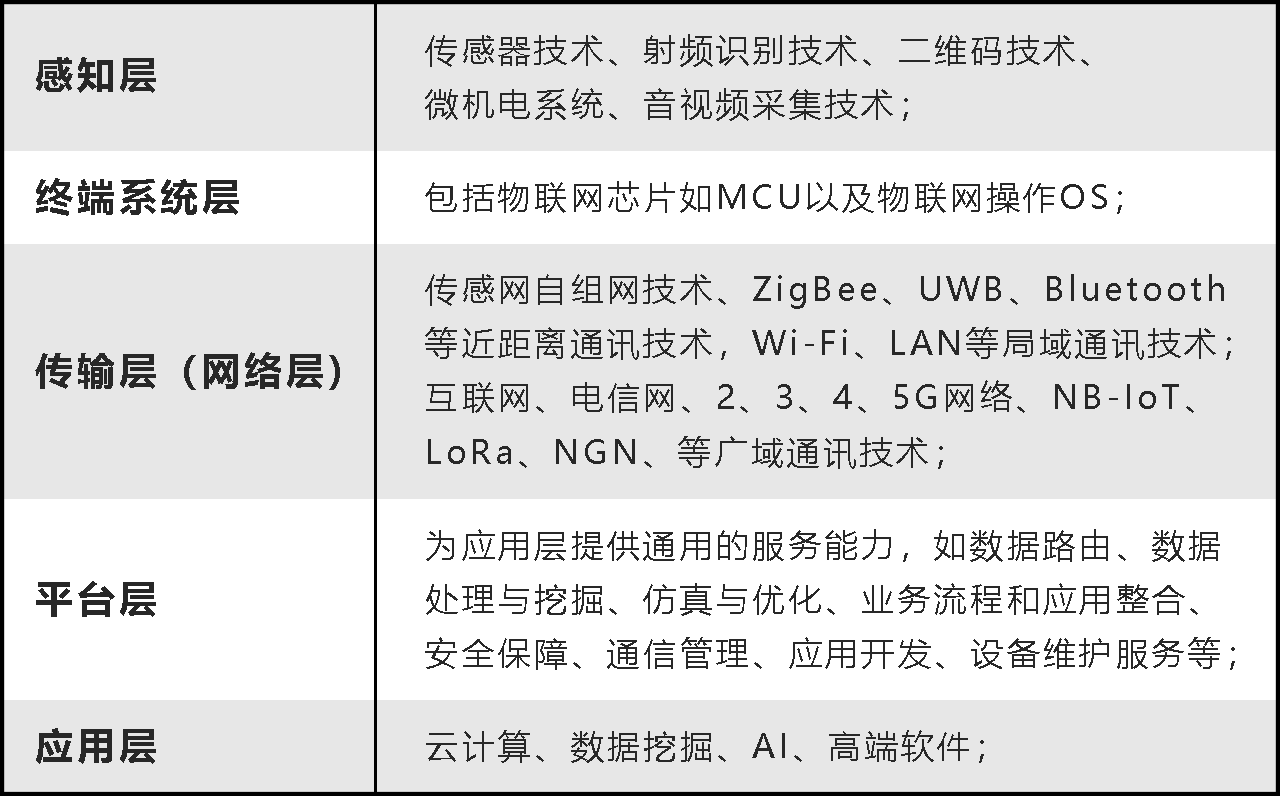
The IOT system can be roughly divided into perception layer, terminal system layer, network layer (further divided into network access layer and core layer), equipment management layer, background application layer and so on. Because it contains a large number of embedded devices, compared with the traditional single device, the Internet of things faces the problem of fragmentation. Both the bottom connection and the upper application services emphasize that 'the technology industry has expertise':
Requirements of Internet of things on operating system
The IOT system requires smaller devices in the sensing layer, lower power consumption, safety, reliability and networking capability;
The communication layer of the Internet of things needs to support various communication protocols and the conversion between protocols;
The application layer needs cloud computing capability.
In terms of software, the previous embedded operating system only completed the abstraction of physical hardware, and can not really represent the future Internet of things. For example, in the Android ecological environment, developers basically do not need to consider the physical hardware configuration of the intelligent terminal. They just need to write applications according to the Android programming interface to run on all Android based intelligent terminals.
In short, this is the difference between 'Internet of things device operating system' and 'Internet of things operating system'. The device operating system solves the problem of how to network devices and how to network more conveniently, but it does not solve the problem of what to do and how to do after networking. For the whole Internet of things system, the latter is more important.
Supporting the Internet of things system requires more complex software than traditional embedded devices. It can not be simply limited to the 'edge side operating system', but involves many levels, such as chip layer, terminal layer, edge layer, cloud layer and so on. The purpose of scheduling the 'object' itself is achieved through layer by layer distribution and release, and by scheduling the computing resources of different devices at different levels such as cloud, edge and end. These requirements give birth to a special operating system for Internet of things devices and applications.
Characteristics of Internet of things operating system
The IOT operating system has the following characteristics in the application field of IOT:
1. Kernel size scalability and architecture scalability
The development of the Internet of things is about to enter a small explosive period. Therefore, in the face of rounds of technological innovation and even replacement, the flexibility and scalability of the overall architecture can be said to determine the business lifeline of an enterprise. At the same time, in order to meet the technical requirements in different application scenarios, the scalability of kernel size is also a problem to be faced.
2. Real time performance of kernel
For the non preemptive scheduling kernel, it is difficult to meet the real-time requirements of key actions, such as common interrupt response and multi task scheduling, the real-time requirements of the operating system have higher requirements, especially for most Internet of things applications, the intentional response time determines the market acceptance.
3. Safety and reliability
In the application environment of the Internet of things, in the face of a large number of nodes, it can be said that once the equipment is put into use, it is difficult to maintain it. Therefore, MTBF and performance in some harsh environments are particularly important. The data security of confidential institutions that have always paid great attention to information security has triggered extensive discussions in the industry on open source mechanism and VMM mechanism.
4. Low power consumption
Due to the increasing number of application scenarios and network nodes of the Internet of things, low power consumption is a very key indicator. Therefore, when designing the overall architecture, it is necessary to add some logical judgments such as sleep mode, energy-saving mode and frequency reduction mode to extend the endurance.
Inventory of mainstream IOT operating systems
The real operating system developed for the characteristics of the Internet of things was riot (real-time multitasking operating system) in 2010. Subsequently, in 2014, Wind River (acquired by Intel) announced VxWorks 7 Internet of things operating system at the embedded World Conference in Nuremberg, Germany. Also in 2014, arm launched the Internet of things device platform and operating system mbed OS. Later, Microsoft launched the operating system Windows 10 IOT core for the Internet of things on the basis of windows 10.
Shanghai Qingke was the first to release the Internet of things operating system in China, and mico was released three months earlier than arm. After the failure to lay out the mobile operating system, Alibaba Yun OS also began to turn to the Internet of things. In 2015, Huawei also launched the open source IOT OS liteos, and the harmony OS, which appeared after the US sanctions, contains the software code of liteos and has become the underlying operating system of Huawei in the field of intelligent devices.
At present, the operating systems of the Internet of things are mainly divided into two categories. One is developed from the traditional embedded RTOS, which are typically represented by FreeRTOS, liteos, RT thread and arm mbed OS; Second, it is extended from the cloud platform of Internet companies and 'tailoring' and customization based on traditional operating systems. Typical representatives include Ali OS things, tencentos tiny and win10 IOT.
The advantage of RTOS camp is that it has been widely supported on IOT terminals and the hardware promotion cost is low. The disadvantage is that the software development is highly professional, and the software and hardware development is difficult to isolate, which makes it difficult for professional software companies to enter this field.
The advantage of the Internet platform camp is that it is naturally combined with Internet services to facilitate the docking of Internet applications. The disadvantage is that basically, each product is independent of each service, so it is difficult to be platform neutral, and the functionality is limited for software developers.
According to the foreign and domestic camps, this paper makes an inventory of the existing active Internet of things operating systems. Those operating systems that are relatively small, have appeared briefly and then faded out or are no longer updated are beyond the scope of this article.
ABROAD
Wind River - VxWorks

VxWorks operating system is an embedded RTOS designed and developed by Wind River in 1983. It is a key part of tornado embedded development environment. Good sustainable development ability, high-performance kernel and friendly user development environment gradually occupy a place in the field of embedded real-time operating system.
VxWorks supports almost all embedded CPUs in modern markets, including x86 series, MIPs, loongisa, PowerPC, Freescale ColdFire, Intel i960, SPARC, SH-4, arm, StrongArm and Xscale CPUs. Other features include a tailorable microkernel structure; Efficient task management; Flexible inter task communication; Microsecond interrupt processing; Support POSIX 1003.1b real-time extension standard; Support a variety of physical media and standard and complete TCP / IP network protocols.
However, it is expensive. Since the operating system itself and the development environment are proprietary, the price is generally relatively high. It usually takes more than 100000 yuan to build a usable development environment, and royalties are generally charged for each application. Generally, the source code is not available, only binary code is provided. Because they are special operating systems and require special technicians to master development technology and maintenance, the cost of software development and maintenance is very high. The number of supported hardware is limited.
Canonical - Ubuntu Core

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution based on desktop applications, which is very popular among players and makes the Ubuntu core specially built for the Internet of things released in November 2016 popular. Ubuntu core is a lightweight operating system and is designed with the concept of 'security first'. According to official documentation, the entire system has been redesigned to focus on security from the first start.
Ubuntu core is tamper proof. Because applications may come from different sources, they only have privileges on their own data. This is done so that a poorly designed application does not make the entire system vulnerable. Ubuntu core is built for business, which means that developers can focus directly on the application at hand, while other requirements are supported by the default operating system.
Another important feature of Ubuntu core is the availability of secure app store and an off the shelf software ecosystem, so it is easier to use Ubuntu core.
RIOT

Riot was originally developed by Fu Berlin, INRIA and haw Hamburg. Riot is based on micro kernel architecture, and its kernel is basically inherited from firekernel; This kernel was originally developed for sensor networks.
Unlike other low memory consuming systems such as TinyOS and Contiki, riot allows applications to be written in C language and C + + language, and provides a complete multi-threaded and real-time response solution. This makes riot a 'user-friendly Internet of things operating system', which supports many low-power IOT devices and various microcontroller architectures.
Its friendliness to developers is reflected in its support for standard environments and tools, so developers do not need to go through a steep learning process. Support standard programming languages, such as C or C + +, and there is very little hardware related code. Developers can write code once, and then run it on 8-bit, 16 bit and 32-bit MCU. Riot can also be used as a
Riot is also resource friendly and Internet of things friendly. One of its important functions is its ability to support light equipment, which can achieve large energy consumption. It supports multithreading with little thread overhead. Riot provides a variety of communication protocol stacks, including IPv6, 6LoWPAN and content center network. It also supports RPL, UDP, TCP, and COAP.
Contiki

Contiki's name comes from a sailboat, Kon Tiki, made by Thor Heyerdahl, one of the most famous explorers in history. Its basic kernel and most of its core functions were developed by Adam dunkels of the network embedded system group of the Swedish Institute of computer science.
Contiki is a small, open source and easily portable multitasking operating system, especially for embedded systems with limited memory. From 8-bit computer to microcontroller, Contiki can provide multitasking environment and built-in TCP / IP support with only thousands of bytes of code and hundreds of bytes of memory. In a typical configuration, Contiki system only needs 2KB ram and 40KB ROM.
Contiki includes an event driven kernel, so the upper application can be loaded dynamically at run time. Contiki uses the lightweight protothereads process model to provide a linear, thread like programming style on the event driven kernel.
Arm - Mbed OS

Mbed OS is a single threaded Internet of things operating system, which was developed by arm and its technical partners. The latest version is upgraded to mbed OS 5 and integrates the kernel of real-time operating system cmsis-rtos RTX, so that mbed OS can support deterministic and multi-threaded real-time programs, such as industrial automation control with low delay and Internet of vehicles.
Mbed OS 5 can run on all Cortex-M series products and has good scalability. If you are dealing with product applications with low performance requirements, you can only retain the core functions of mbed OS 5 so that it can run on Cortex-M0 chip with only 8K memory.
Applications for the mbed platform can be developed using the mbed online IDE, which is a free online code editor and compiler. Just install a web browser on the local PC, because your project is compiled in the cloud, that is, use the armcc C / C + + compiler on the remote server. The mbed ide provides a private workspace with the ability to import, export and share code through distributed mercurial version control, and it can also be used for code document generation. Applications can also be developed using other development environments, such as keil µ vision, IAR embedded workbench, eclipse and GCC ARM embedded tools.
Keil - RTX
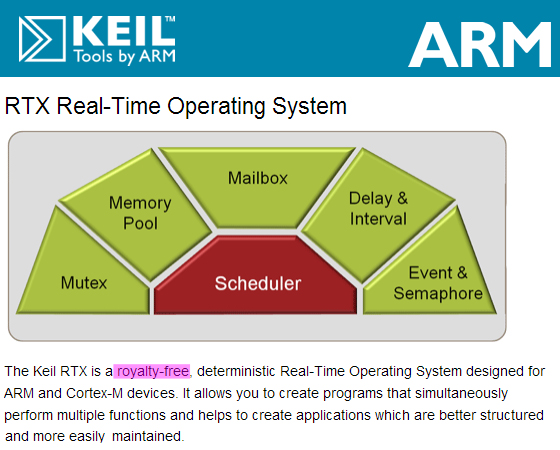
RTX operating system is an embedded real-time operating system developed and upgraded by keil company (which has been incorporated into arm). It is written in standard C structure and compiled with RealView compiler. It is suitable for arm Cortex-M equipment. It is not only a real-time kernel, but also has rich middle tier components. It is not only free, but also the code is open.
The main functions of RTX are to start and stop tasks (processes). In addition, it also supports process communication, such as task synchronization, management of shared resources (peripherals or memory), and message transmission between tasks. Developers can use basic functions to start the real-time runner, start and end tasks, and transfer control between tasks (round robin scheduling). Developers can give priority to tasks.
It is characterized by supporting time slice, preemptive and cooperative scheduling. There is no limit to the number of tasks, and each task has a priority of 254. Unlimited number of semaphores, mutually exclusive semaphores, message mailboxes and soft timers. Supports multithreading and thread safe operations. Using the MDK dialog based configuration wizard, you can easily complete the MDK configuration.
University of California, Berkeley - TinyOS

TinyOS was originally a cooperation project developed by the University of California, Berkeley and Intel Research to embed intelligent micro dust, and then gradually evolved into an international cooperation project, namely TinyOS alliance. TinyOS is written in NESC language. It is an open source operating system. It is based on a component based architecture, which enables the rapid implementation of various applications.
TinyOS was originally designed to make an exclusive embedded wireless sensor network (WSN) operating system. But in fact, TinyOS also occupies a very important position in the application field of the Internet of things due to its good scalability and small enough code size.
TinyOS's user community is very active, and its users are all over academia and industry. The popularity of TinyOS can be understood from the fact that TinyOS has been downloaded more than 35000 times a year. TinyOS is very effective in various scenarios, such as sensor networks, intelligent buildings, smart meters, etc.
Amazon - FreeRTOS

FreeRTOS is a mini real-time operating system kernel designed by Richard Barry in 2003. As a lightweight operating system, the whole core code has only 3 to 4 C files. In order to make the code easy to read, transplant and maintain, most of the code is written in C language, and only some functions (mostly architecture specific scheduling subroutines) are written in assembly language.
It is characterized by user configurable kernel function, multi platform support, small object code, simple and easy to use, powerful execution tracking function, stack overflow detection, unlimited number of tasks and task priority. Multiple tasks can be assigned the same priority, queue, binary semaphores, counting semaphores, recursive communication and synchronous tasks and priority inheritance.
FreeRTOS provides many methods to implement threads, tasks, mutexes, semaphores and software timers. It has a tick less mode for low power consumption applications, and thread priority management is also supported. The main functions include: task management, time management, semaphore, message queue, memory management, recording function, software timer, collaboration, etc., which can basically meet the needs of small systems.
The operating system is simple and easy to use. At present, many manufacturers use this foreign system on lightweight CPU, and it has been successfully transplanted to 35 different microcontrollers. FreeRTOS is licensed under the MIT license.
Microsoft - Windows 10 IoT
Windows was once called Windows Embedded, which is Microsoft's embedded product family. Microsoft renamed 'Windows Embedded' to 'windows IOT' when it began to release the embedded version of windows 10. The system aims at a variety of Internet of things devices, from small industrial gateways to larger and more complex devices (such as control medical devices and ATM). It is suitable for embedded devices such as automated manufacturing, retail, medical, military, finance and aerospace.
At present, it includes four series: Windows Embedded standard, Windows Embedded compact, Windows Embedded enterprise and windows embedded posready.
In May 2020, Microsoft announced that it would combine the two versions of windows 10 IOT core and windows 10 IOT enterprise into one. It is expected to release the first version in 2021. At the same time, it also promised that the new version will be more streamlined and add the implementation of new functions such as Linux container.
Google - Fuchsia

In 2016, Google was exposed to be developing an Internet of things OS called 'Fuchsia' based on the micro kernel zircon. It is speculated that fuchsia is Google's attempt to unify the whole ecosystem with a single operating system, that is, an operating system can run on devices such as smart watches, smart speakers, laptops and smart phones.
Different from Chrome OS and Android based on Linux kernel, fuchsia is based on a new micro kernel named zircon, inspired by little kernel and used in embedded systems. It is mainly written in C language and C + +.
Fuchsia's user interface and applications are developed using 'flutter'. Thanks to the cross platform capability provided by flutter, users can install some Fuchsia on Android devices.
Fuchsia's image logo is a pink infinite symbol. As free and distributed, three sentence versions of BSD, MIT and Apache 2.0 software licenses are adopted.
Linux foundation - Zephyr

Zephyr was originally the 'rocket kernel' developed for Internet of things devices launched by Fenghe system company in November 2015. Earlier, it was called 'microkernel profile for VxWorks'. The code was transplanted to virtuoso DSP RTOS obtained from the acquisition of eonic systems in 2001. In February 2016, it became a project of the Linux foundation and changed its current name.
Zephyr is a small real-time operating system that supports a variety of architectures and is optimized for resource constrained environments. It is suitable for everything from simple embedded environment sensors and led wearable devices to complex smart watches and IOT wireless gateways. The main functions of zephyr are listed below:
Support more than 150 boards.
Complete flexibility and freedom of choice.
It can handle small Internet of things devices.
You can develop products with built-in security features.
Security is also important in zephyr design, and a special mechanism is set up to maintain or improve security.
Micrium-μC/OS-II 
μ C / OS is provided by Micrium company. It is a portable, curable, tailorable, preemptive and multitasking open-source real-time kernel. It is designed for embedded applications and can be used for 8-bit, 16 bit and 32-bit MCU or digital signal processor (DSP). μ C / OS - Ⅱ is in the original version μ Major improvements and upgrades have been made on the basis of C / OS. At present, it has been upgraded to μ C/OS-III。 The source code is open, tidy, consistent, and annotated in detail. It is suitable for system development. It has been used for nearly ten years, and there are many examples of successful application of the real-time kernel.
μ The main features of C / OS - Ⅱ are as follows:
Open source code makes it easy to transplant the operating system to different hardware platforms; Portability, most of the source code is written in C language, which is easy to transplant to other microprocessors;
Curable;
Tailoring and selective use of required system services to reduce the storage space required by the bucket;
Preemptive, completely preemptive real-time kernel, that is, the task with the highest priority under the condition of running readiness;
Multi task, 64 tasks can be managed, the priority of tasks must be different, and the time slice rotation scheduling method is not supported;
Determinacy: the execution time of function call and service has its determinacy, which does not depend on the number of tasks;
Practicability and reliability, the example of successful application of the real-time kernel is the best evidence of its practicability and reliability.
Strictly speaking, μ C / OS is only a real-time operating system kernel. It only contains the basic functions of task scheduling, task management, time management, memory management, communication and synchronization between tasks. No additional services such as input / output management, file system and network are provided. However, due to the good scalability and open source of UC / OS, these non essential functions can be realized by users according to their needs.
Embedded Linux

Embedded Linux is the general name of a kind of embedded operating system. This type of operating system is based on the Linux kernel and is designed to be used in embedded devices. Because its source code is open, people can modify it arbitrarily to meet their own applications, and it is easy to check errors. GPL compliance eliminates the need to pay a license fee for each application. There are a large number of application software available, most of which comply with GPL, are open source and free, and can be applied to the user's own system after a little modification.
In addition, there are a large number of free and excellent development tools that comply with GPL and are open source. There is a large group of developers, no need for special talents, as long as they understand UNIX / Linux and C language. With the popularity of Linux in China, there are more and more such talents. Therefore, the cost of software development and maintenance is very low. In addition, stable network function is a great advantage of Linux itself. The kernel is compact and requires less resources to run. A typical embedded Linux installation requires about 2MB of system memory.
There is no essential difference between embedded Linux and ordinary Linux. Almost all hardware used on PC supports embedded Linux. Moreover, the driver source code of various hardware can be obtained, which brings great convenience for users to write their own proprietary hardware drivers.
One disadvantage of running Linux on the system is that the Linux system needs to add real-time software modules to provide real-time performance. The kernel space of these modules is the part of the operating system to realize scheduling strategy, hardware interrupt exception and execution program. Because these real-time software modules run in kernel space, code errors may destroy the operating system and affect the reliability of the whole system, which will be a very serious weakness for real-time applications.
RIM - QNX

QNX is mainly aimed at the embedded system market. Although it does not belong to QNX, due to its support, most traditional UNIX programs can be compiled and executed on QNX after minor modification (or even no modification). It is a commercial real-time operating system. The product was developed in the early 1980s and later renamed QNX software systems. The company has been acquired by research in motion (rim, blackberry manufacturer).
QNX is one of the most successful microkernel operating systems. Most functions are executed by many small tasks, which are called server. This architecture allows users and developers to turn off unwanted functions without changing the operating system itself.
QNX neutrino (2001) has a micro internal verification platform, which is real-time, stable, reliable and fast. It has been transplanted to many platforms and runs on various modern processors used in the embedded market, such as x86, PowerPC, etc. QNX has been widely used in the automotive field, such as the music and media control system of Porsche sports cars, the control system of the unmanned crush tank of the U.S. Army, and the BlackBerry PlayBook tablet of rim.
Nucleus

Nucleus real time operating system (nucleus RTOS) is an embedded operating system launched by accelerated technology under mentor graphics (renamed Siemens EDA). The advantage of nucleus is that programmers no longer need to write boards to support package software (BSP), and about 95% of the code is written in ANSI C. It is very easy to transplant and can support most types of processors. At the same time, it can provide module support such as network, graphical user interface and file system.
In a typical target environment, the core code area of Nucleus Plus generally does not exceed 20K bytes. From the implementation point of view, Nucleus Plus is a group of C function libraries. The application code is connected with the core function library to generate an object code, which can be downloaded to the ram of the object board or directly burned to the ROM of the object board for execution. Due to the software component method, each component of Nucleus Plus is very easy to replace and reuse. The components of Nucleus Plus include task control, memory management, inter task communication, task synchronization and mutual exclusion, interrupt management, timer and I / O driver.
Nucleus RTOS provides strictly annotated C source code to every user.
Microsoft - ThreadX

ThreadX is a real-time operating system developed by American Express logic company (acquired by Microsoft in 2019). The author of ThreadX is Willian Lamie, who was also the author of nucleus and the CEO of express logic.
ThreadX's name comes from two aspects. Thread is the executable unit of the operating system, and 'X' indicates context switching. Threads of ThreadX share the same memory space, and resources can be shared.
Similar to many other real-time operating systems, ThreadX is a multitasking system, which adopts preemptive scheduling, fast interrupt response, independent memory management, and supports inter thread communication, mutual exclusion, event and thread synchronization.
ThreadX is mainly characterized by supporting priority inheritance, preemption threshold design, microkernel design, small code space, etc. ThreadX source code adopts royalty free usage mode.
ThreadX is usually used in embedded operating systems. Most of the development work is completed on the host, which runs windows or Linux system. The cross compiler can generate the machine code of the target system on the host, and then download it to the target board to run.
Several development tools that can recognize ThreadX system (OS aware), including wind river workbench, arm RealView, Greenhills software's multi, Metrowerks CodeWarrior, IAR c-spy, Lauterbach trace32 and visionclick.
ThreadX supports architectures including arm, x86, arc, MIPs, xtensa, etc., covering almost all mainstream CPU architectures
DOMESTIC
Huawei - LiteOS

Huawei liteos was released in 2015, and the open source version was launched in September 2016. The kernel source code is open-source, with a size of only 10K. It is a lightweight Internet of things operating system launched by Huawei for the Internet of things and an important part of Huawei's Internet of things strategy. It has the key capabilities of lightweight, low power consumption, interconnection, rich components and rapid development, creates a domain technology stack based on the business characteristics of the Internet of things, provides developers with a 'one-stop' complete software platform, effectively reduces the development threshold and shortens the development cycle, and can be widely used in wearable devices, smart homes, Internet of vehicles, lpwa and other fields.
Key features include low-power framework, opencpu architecture, security design, end cloud interworking components and SOTA remote upgrade.
Huawei Hongmeng harmonyos (including liteos kernel)

Huawei harmonyos is a distributed operating system for all scenarios (mobile office, sports and health, social communication, media entertainment, etc.). Based on the traditional single device system capability, harmonyos puts forward a distributed concept based on the same set of system capability and adapting to multiple terminal forms, which can support multiple terminal devices. The main feature of harmonyos is distributed, including soft bus, device virtualization, data management and task scheduling. At the same time, it has one-time development and multi terminal deployment; Unified OS and flexible deployment.
Harmonyos mainly includes Linux, harmonyos kernel and Lite OS. Liteos is adopted by default, and the words liteos-a and liteos-m can be seen in the harmonyos kernel file. It is speculated that the harmonyos kernel has certain inheritance to the liteos kernel. Multi kernel design can select the appropriate kernel when supporting different resource constrained devices. From another point of view, liteos kernel is not limited to harmonyos, and the supported hardware is even richer than harmonyos. It provides more kernel cases and migration strategies. From the code point of view, they all support Cortex-M kernel and cortex-a kernel.
Little question: what's the difference between liteos and Hongmeng
Due to their different product positioning, they also have different consumption of memory and resources.
Because Huawei liteos has high clipping characteristics, it only retains the kernel when hardware resources are limited. It can be clipped to 6KB ROM and consume 2KB ram resources. It can be said that the resource consumption is low to a certain extent. In order to ensure the system performance requirements, harmonyos requires 128K ROM and 2MB ram for hardware resources.
Therefore, Huawei liteos focuses on the business field of Internet of things, which is more suitable for the application scenario of low hardware configuration, low cost and low power consumption; Harmonyos is more suitable for multimedia interaction and complex applications that require JS to increase development efficiency. At present, the development board of harmonyos mainly supports Huawei's self-developed chips. Huawei liteos not only supports Huawei's self-developed chips, but also supports the mainstream arm development learning board in the market.
Alibaba - AliOS Things

Alibaba OS originated from the mobile operating system yunos, which has been nearly 10 years ago. Later, it was integrated and upgraded to Alios. Among them, Alios things is a highly tailorable and lightweight embedded operating system of Alios family dedicated to the field of Internet of things, which is committed to building cloud integrated Internet of things infrastructure. It has extreme performance, minimalist development, cloud integration, rich organization, security protection and other key capabilities, and supports the connection of terminal devices to Alibaba cloud link, which can be widely used in smart home, smart city, new travel and other fields.
In October 2017, Alios things was officially open source.
Alios things adopts micro kernel architecture and can container and online upgrade the software running on intelligent hardware, which means that the software and hardware can be decoupled and operated quickly, reducing the production and maintenance costs of hardware manufacturers. According to Ali's official introduction, this is an operating system dedicated to aiot intelligent devices. It has the characteristics of new development mode, online cutting tool, separation of application and kernel, script language support, local AI framework and so on.
In addition, Alios things is also the core of the yoc software platform.
Ruisaide - RT-Thread

RT thread, released in 2006, is a technical platform integrating RTOS kernel, middleware components and developer community. It is developed under the leadership of Mr. Xiong Puxiang and the strength of the open source community. RT thread is also an Internet of things operating system with complete and rich components, high scalability, easy development, ultra-low power consumption and high security. RT thread has all the key components required by an IOT operating system platform, such as GUI, network protocol stack, secure transmission, low-power components, etc.
Official data show that RT thread currently has the largest embedded open source community in China. At the same time, it is widely used in many industries such as energy, vehicle, medical treatment and consumer electronics, with a cumulative installed capacity of more than 800 million units. It has become an open source RTOS independently developed by Chinese people, the most mature and stable in China and the largest installed capacity.
RT thread has a good software ecology, supports all mainstream compilation tools on the market, such as GCC, KEIL, IAR, etc., has a complete and friendly tool chain, and supports various standard interfaces, such as POSIX, CMSIS, C + + application environment, JavaScript execution environment, etc., which is convenient for developers to transplant various application programs. Commercial supports all mainstream MCU architectures, such as arm Cortex-M / R / A, MIPs, x86, xtensa, c-sky, risc-v, and almost all mainstream MCU and Wi Fi chips in the market.
China Mobile IOT - OneOS

Oneos is a lightweight operating system launched by China Mobile for the Internet of things. The top-level design began in 2018 and the open-source version was officially released in June 2020. The system has the characteristics of tailorability, cross platform, low power consumption and high security. It supports mainstream CPU architectures such as arm Cortex-M / R / A, MIPs and risc-v, is compatible with standard interfaces such as POSIX and CMSIS, supports the development of micro Python language, and provides graphical development tools, which can effectively improve the development efficiency and reduce the development cost, and help customers develop stable, reliable Secure and easy-to-use Internet of things applications.
Oneos follows Apache license version 2.0. Individual and enterprise customers can use it in commercial products free of charge. There is no need to publish the source code and there is no potential commercial risk. China Mobile Internet of things said that it would uphold an open and cooperative attitude and provide customers with stable systems suitable for various Internet of things scenarios free of charge.
Tencent - TencentOS tiny

Tencentos tiny is a real-time operating system developed by Tencent in the field of Internet of things. It has the characteristics of low power consumption, low resource occupation, modularity, safety and reliability, and can effectively improve the development efficiency of Internet of things terminal products.
Tencentos tiny is known as the smallest in the industry, with only 1.8K. It provides a simplified RTOS kernel. The kernel components can be tailored and configured, and can be quickly transplanted to a variety of mainstream MCU and module chips. Rich IOT components are provided based on RTOS kernel, and mainstream IOT protocol stacks (such as COAP / mqtt / TLS / dtls / lorawan / Nb IOT) are integrated internally, which can help IOT terminal devices and services quickly access Tencent cloud IOT platform.
Interestingly, shortly after the launch of this operating system, Tencent announced that tencentos would stop service on June 28, 2017. The explanation given at that time was, 'because the third-party ROM market is shrinking, tencentos is going to withdraw from the stage of history.'
However, facing the prospect of the Internet of things market, Tencent announced the open source of tencentos tiny in September 2019, hoping to further promote the prosperity of its Internet of things ecology. At present, tencentos tiny has supported a variety of chips and modules from mainstream manufacturers such as Italy France semiconductor, NXP, Huada semiconductor, Ruixing Hengfang and national technology. However, compared with the strong and comprehensive ecological layout of Huawei and Alibaba, Tencent still has a long way to go.
Qingke - MiCO

In July 2014, Shanghai mxchip and Alibaba cloud released mico (micro controller based Internet connectivity operating system), which is a highly portable operating system and middleware development platform for intelligent hardware optimization design and running on microcontrollers. At that time, Qingke said that this was China's first real Internet of things operating system.
As an independent system, mico has an open architecture, does not depend on MCU models, and has a hardware abstraction layer (HAL). In addition, the application open interface of firmware has implemented a variety of application layer protocols: Haier, Midea, Ao, apple MFI, homekit, Siri voice control, etc. Mico includes the underlying chip driver, wireless network protocol, RF control technology, security, application framework and other modules.
Mico contains a real-time operating system kernel for IOT devices, which is suitable for running on micro control devices with limited resources. In addition, mico also includes network communication protocol stack, security algorithms and protocols, hardware abstraction layer, programming tools and other essential software function packages for developing IOT. Mico provides the abstraction of MCU platform, so that mico based application development does not need to care about the realization of MCU specific functions, and quickly build the software in IOT equipment through various programming components provided in mico.
Wing glow - SylixOS 
Sylixos is a large embedded hard real-time operating system independently designed and developed by Yihui information. It has been developed since 2006. According to the evaluation report of the Ministry of industry and information technology, the kernel autonomy rate is 100%. It supports symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) platform, has rich file system, network system and many device driver support, and provides a perfect integrated development environment. The application fields mainly include network equipment, national defense security, industrial automation, rail transit, electric power, medical treatment, aerospace, automotive electronics, etc.
Globally, as a latecomer of real-time operating system, sylixos draws on the design ideas of many real-time operating systems, including RTEMS, VxWorks, ThreadX, etc. Its birth can get rid of the dependence of some key domestic equipment on foreign embedded operating systems, and provide a new choice for the domestic embedded information technology industry.
In order to ensure the continuous development of sylixos and attract a large number of developers to participate in testing, sylixos currently exists in the form of open source projects. According to the official website, the source code of the operating system has been authorized to a number of domestic scientific research institutions, including China Aerospace Science and industry group, China Aerospace Science and technology group, Longxin Zhongke, National University of Defense Science and technology, and has launched sylixos Seahawk Yihui, Fengyun Yihui, Longxin Yihui, Qilin Yihui and other distribution versions.
At present, the domestic Internet of things operating system can be described as a hundred flowers bloom. In addition to the above, there are oasis OS of Xinhua San, uhomos of Haier, deltaos (Tao system) of keyin Jingcheng, djyos of Qin Jian computer, aworks OS of Zhiyuan electronics, AcoreOS (Tianmai) of AVIC Computing Institute, hopenos of Kaisi haopeng, etc. However, generally speaking, most of the global Internet of things market is dominated by foreign operating systems, especially American companies that entered the market earlier, such as ThreadX, FreeRTOS, VxWorks, etc.
Summary
At present, in the Internet of things operating system market, in addition to the products of some old foreign manufacturers, more than a dozen other products are in the early stage of development, and there is no monopoly environment of one or several OS in the industrial chain. For Internet manufacturers who have ecology and are not short of money, many still want to use their own customized OS, which has also caused mountains in the industry to a certain extent.
On the other hand, open source Linux and RTOS are still the mainstream of the Internet of things market. In addition to enterprises with their own OS, most of the other manufacturers adopt open-source and neutral third-party operating systems with ecological advantages, such as RT thread.
The operating system cannot exist as a single product, but should be an ecosystem, which needs the support of hardware and software developers. Windows and Android systems have taken the lead in the PC era and smart phone era, forming a monopoly, which makes it difficult for latecomers to subvert. They look forward to the next wave of computing revolution.
According to the market analysis of BCG Boston Consulting, about 80% of the winners have obtained more than 50% of the market share in the first five years. They use an average of 7 years to reach the peak of the market share, with a market share of about 80%. In contrast to the data of losers, their average market share in the first five years was 8%, and the peak was only 13%. For example, Microsoft's Windows Phone and blackberry operating systems have a peak market share of only 15%.
Today, more new opportunities are opening up in the Internet of things operating system market. The old overlords may not be able to continue their hegemony in the Internet of things era. Only by seizing the opportunity to rapidly expand their scale and grasp the first mover advantage can emerging players occupy the commanding heights of the Internet of things Era. If you can't quickly expand your market share, you may be out if you don't even have the qualification to participate.
In various emerging markets, overseas enterprises do not have absolute advantages, which creates opportunities for domestic enterprises to develop their own operating systems. For example, Huawei, Xiaomi, bat and other domestic enterprises with extensive layout of intelligent hardware and IOT have also promoted the rise of domestic IOT operating systems to a certain extent.